App - SharpData
SharpData is a generic app for providing an instant UI around multiple RDBMS's:
YouTube: youtu.be/GjVipOqwZMA
It makes use of the app dotnet tool for running Chromium Gist Desktop Apps on-the-fly without installation, from a single URL that can also mix in additional gists which can be used in SharpData to configure RDBMS's, copy SQLite databases and apply per-database customizations to add navigable deep links and customized UI Views to each table resultset.
Whilst SharpData supports connecting to most popular RDBMS's, it's especially useful for being able to deploy an instant stand-alone UI with an embedded SQLite databases which can be published independently in a gist and launched from a single URL.
For an example of this in action we've published customized gists for the Northwind and Chinook SQLite databases which after installing the latest app dotnet tool:
$ dotnet tool install -g app
$ app -version
First time app is run it registers the app:// URL scheme allowing Windows x64 Desktop Apps to be launched from URLs:
Or via command-line:
$ app open sharpdata mix northwind.sharpdata
$ app open sharpdata mix chinook.sharpdata
Cross platform using the x dotnet tool (in Default Browser):
$ x open sharpdata mix northwind.sharpdata
$ x open sharpdata mix chinook.sharpdata
Each of these options will download & run the latest version of SharpData along with a copy of the northwind.sharpdata or chinook.sharpdata gists on-the-fly containing the embedded SQLite DB along with any UI customizations.
Hosted as a .NET Core App
As NetCoreApps/SharpData is also a standard .NET Core project, it can also be deployed as a normal stand-alone .NET Core Web App:
https://sharpdata.netcore.io
Tiny footprint
An impressively capable .NET Core App that fits into a tiny 20kb .zip footprint thanks to Gist Desktop App's Architecture. It's small dynamic #Script & Vue TypeScript code-base also makes it highly customizable to tailor & further extend with
App-specific requirements - suitable for offering advanced system users a quick, capable customized read-only UI of your DBs.
SharpData started as a demonstration showing how productive #Script can be in the number of areas where dynamic languages offer far superior productivity then the typical .NET approach of using C# to type an entire code-base & models.
For example a single #Script page provides a lot of the functionality in AutoQuery where it provides an instant HTTP API
(in all registered ServiceStack formats) around all registered RDBMS tables, in all OrmLite supported RBDMS's, that includes support for custom fields,
multiple querying options, paging, multi OrderBy's in a parameterized SQL query executed with OrmLite's SQL async DB APIs:
AutoQuery Script
/db/_db/_table/index.html
{{ {namedConnection:db} |> if (db && db != 'main') |> useDb }}
```code|quiet
var ignore = ['db','fields','format','skip','take','orderBy']
var fields = qs.fields ? qs.fields.split(',').map(x => sqlQuote(x)).join(',') : '*'
var sql = `SELECT ${fields} FROM ${sqlQuote(table)}`
var filters = []
var queryMap = qs.toObjectDictionary().withoutKeys(ignore)
#each queryMap.Keys.toList()
var search = queryMap[it.sqlVerifyFragment()].sqlVerifyFragment();
#if search == '=null' || search == '!=null'
`${sqlQuote(it)} ${search=='=null' ? 'IS' : 'IS NOT'} NULL` |> addTo => filters
queryMap[it] = null
else if search.startsWith('=')
`${sqlQuote(it)} = @${it}` |> addTo => filters
queryMap[it] = search.substring(1).coerce()
else if search.startsWith('<=') || search.startsWith('>=') || search.startsWith('!=')
`${sqlQuote(it)} ${search.substring(0,2)} @${it}` |> addTo => filters
queryMap[it] = search.substring(2).coerce()
else if search.startsWith('<') || search.startsWith('>')
`${sqlQuote(it)} ${search.substring(0,1)} @${it}` |> addTo => filters
queryMap[it] = search.substring(1).coerce()
else if search.endsWith(',')
`${sqlQuote(it)} IN (${search.trimEnd(',').split(',').map(i=>i.toLong()).join(',')})` |>addTo=>filters
queryMap[it] = null
else if search.startsWith('%') || search.endsWith('%')
`${sqlQuote(it).sqlCast('varchar')} LIKE @${it}` |> addTo => filters
else
`${sqlQuote(it).sqlCast('varchar')} = @${it}` |> addTo => filters
/if
/each
#if !filters.isEmpty()
sql = `${sql} WHERE ${filters.join(' AND ')}`
/if
#if qs.orderBy
sql = `${sql} ORDER BY ${sqlOrderByFields(qs.orderBy)}`
/if
#if qs.skip || qs.take
sql = `${sql} ${sqlLimit(qs.skip,qs.take)}`
/if
sql |> dbSelect(queryMap) |> return
```
{{ ifError |> show(sql) }}
{{htmlError}}
The _ prefixes in the path utilizes Page Based Routing allowing for
CoC based
Clean URL routes without needing to define & maintain separate routes where the
same script supports querying all registered multitenancy databases.
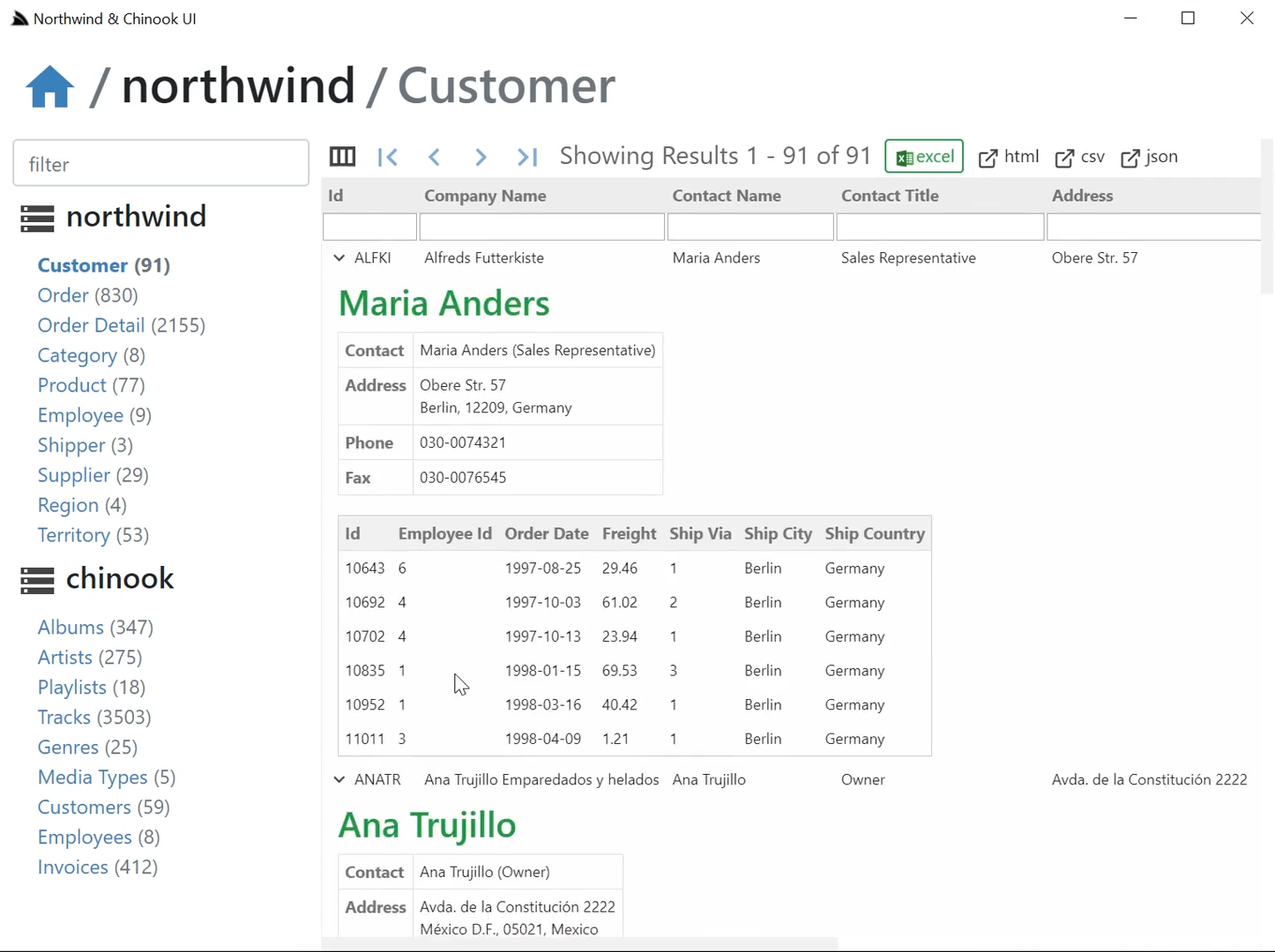
Instant Customizable RDBMS UI
The SharpData project essentially provides a UI around this script, surfacing its features & give it instant utility which ended up being so useful that it's become the quickest way to perform fast adhoc DB queries as it's easy to configure which RDBMS's & tables to show in a simple text file, easy to customize its UI, enables 1-click export into Excel and its shortcut syntax support in column filters is a fast way to perform quick adhoc queries.
Quick Tour
We'll quickly go through some of its features to give you an idea of its capabilities, from the above screenshot we can some of its
filtering capabilities. All results displayed in the UI are queried using the above
sharpdata #Script HTTP API
which supports the following features:
Filters
All query string parameter except for db,fields,format,skip,take,orderBy are treated as filters, where you can:
- Use
=nullor!=nullto searchNULLcolumns - Use
<=,<,>,>=,<>,!=prefix to search with that operator - Use
,trailing comma to perform anIN (values)search (integer columns only) - Use
%suffix or prefix to perform aLIKEsearch - Use
=prefix to perform a coerced "JS" search, for exactnumber,boolean,nulland WCF date comparisons - Otherwise by default performs a "string equality" search where columns are casted and compared as strings
Here's the filtered list used in the above screenshot:
/db/northwind/Order?Id=>10200&CustomerId=V%&Freight=<=30&OrderDate=>1997-01-01
Custom Field Selection
The column selection icon on the top left of the results lets you query custom select columns which is specified using ?fields:
Multiple OrderBy's
You can use AutoQuery Syntax to specify multiple Order By's:
Paging
Use ?skip and ?take to page through a result set
Format
Use ?format to specify which Content-Type to return the results in, e.g:
- /db/northwind/Customer?format=html
- /db/northwind/Customer?format=json
- /db/northwind/Customer?format=csv
Multitenancy
You can specify which registered DB to search using the path info, use main to query the default database:
/db/<named-db>/<table>
Open in Excel
SharpData detects if Excel is installed and lets you open the un-paged filtered resultset directly by clicking the Excel button
This works seamlessly as it's able to "by-pass" the browser download where the query is performed by the back-end .NET Core Server who streams the response directly to the Users Downloads folder and launches it in Excel as soon as it's finished.
Launching SharpData
To run SharpData in a .NET Core Desktop App you'll need latest app dotnet tool:
$ dotnet tool update -g app
If on macOS/Linux you can use the x dotnet tool instead to view SharpData in your default browser
Configure RDBMS from command-line
You can override which database to connect to by specifying it on the command line, e.g. here's an example of connecting to https://techstacks.io RDBMS:
$ app open sharpdata -db postgres -db.connection $TECHSTACKS_DB
Which will open SharpData listing all of TechStack's RDBMS tables. If you have a lot of tables the Sidebar filter provides a quick way to find the table you want, e.g:
app URL Schemes
What can be done with the open command on the command-line can also be done from a custom URL Scheme, a feature that opens up a myriad of new
possibilities as app can open Gist Desktop Apps from Gists or in public & private GitHub repositories,
where it's able to download and launch Apps on the fly with custom arguments - allowing a single URL to run a never installed Desktop App stored in a
Gist & pass it custom params to enable deep linking.
With this organizations could maintain a dashboard of links to its different Desktop Apps that anyone can access, especially useful as the
only software that's needed to run any Sharp Apps is the app dotnet tool which thanks to all
ServiceStack .dll's & dependencies being bundled with the tool, (including Vue/React/Bootstrap fontawesome and Material SVG Icon assets),
the only files that need to be published are the App's specific resources, which is how Apps like SharpData can be compressed in a
20kb .zip - a tiny payload that's viable to download the latest app each on each run, removing the pain & friction to distribute updates as
everyone's already running the latest version every time it's run.
Should you need to (e.g. large Sharp App or github.com is down) you can run your previously locally cached App using run:
$ app run sharpdata
With Custom URL Schemes everyone with app installed can view any database they have network access to from specifying the db type and connection string in the URL:
app://sharpdata?db=postgres&db.connection={CONNECTION_STRING}
CONNECTION_STRING needs to be URL Encoded, e.g. with JS's
encodeURIComponent()
or by specifying an Environment variable containing the connection string:
app://sharpdata?db=postgres&db.connection=$TECHSTACKS_DB
Mix in Gists
In addition to Sharp Apps being downloaded and run on the fly, they're also able to take advantage of the dotnet tools mix support to also download another Gist's content into the Sharp App's working directory.
With this you can publish a custom dataset in an SQLite database save it as a gist and generate a single URL that everyone can use to download the database and open it in SharpData, e.g:
app://sharpdata?mix=northwind.sqlite&db=sqlite&db.connection=northwind.sqlite
It's possible to use the user-friendly northwind.sqlite alias here as it's published in the global mix.md directory where it links to the northwind.sqlite gist.
For your custom databases you use the Gist Id instead or if you plan to use this feature a lot you can override which mix.md document that
app should source its links from by specifying another Gist Id in the MIX_SOURCE Environment variable (or see below - to create a local alias).
But if you're already mixing in an external gist you may as well include a custom app.settings in the Gist so it's pre-configured with custom
RDBMS registrations and table lists, e.g:
app://sharpdata?mix=northwind.sharpdata
Which applies the northwind.sharpdata gist, which can also be referenced by Gist Id:
app://sharpdata?mix=0ce0d5b828303f1cb4637450b563adbd
Alternatively you may instead prefer to publish it to a private GitHub repo instead of a Gist which anyone can open up with:
app://user/sharpdata-private?token={TOKEN}
The app dotnet tools will use the latest published GitHub release if there are any, otherwise will use the master.zip archive,
this feature can be used to maintain a working master repo and maintain control ver when to publish new versions of your custom SharpData App.
app local aliases
Where ever you can use a Gist Id, you can assign a local user-friendly alias to use instead. So if you had a custom sqlite database and sharpdata app.settings you could assign it to a local db alias with:
$ app alias db 0ce0d5b828303f1cb4637450b563adbd
Which you'll be able to use in place of the Gist Id, e.g. via command-line:
$ app open sharpdata mix db
or via URL Scheme:
app://sharpdata?mix=db
Likewise the gist alias can also be used for referencing Gist Desktop Apps, e.g. we can assign the redis gist app to use our preferred alias:
$ app alias local-redis 6de7993333b457445793f51f6f520ea8
That we can open via command-line:
$ app open local-redis
Or URL Scheme:
app://local-redis
Or if we want to run our own modified copy of the Redis Desktop App, we can mix the Gist files to our local directory:
$ app mix local-redis
Make the changes we want, then run our local copy by running app (or x) without arguments:
$ app
Other alias command include:
View all aliases
$ app alias
View single alias
$ app alias mydb
Remove an alias
$ app unalias mydb
Custom SharpData UI
Each time a Gist Desktop App is opened it downloads and overrides the existing Gist with the latest version which it loads in a Gist VFS where any of its files can be overridden with a local copy.
As the App's working directory is preserved between restarts you can provide a custom app.settings at:
%USERPROFILE%\.sharp-apps\sharpdata\app.settings
Custom app.settings
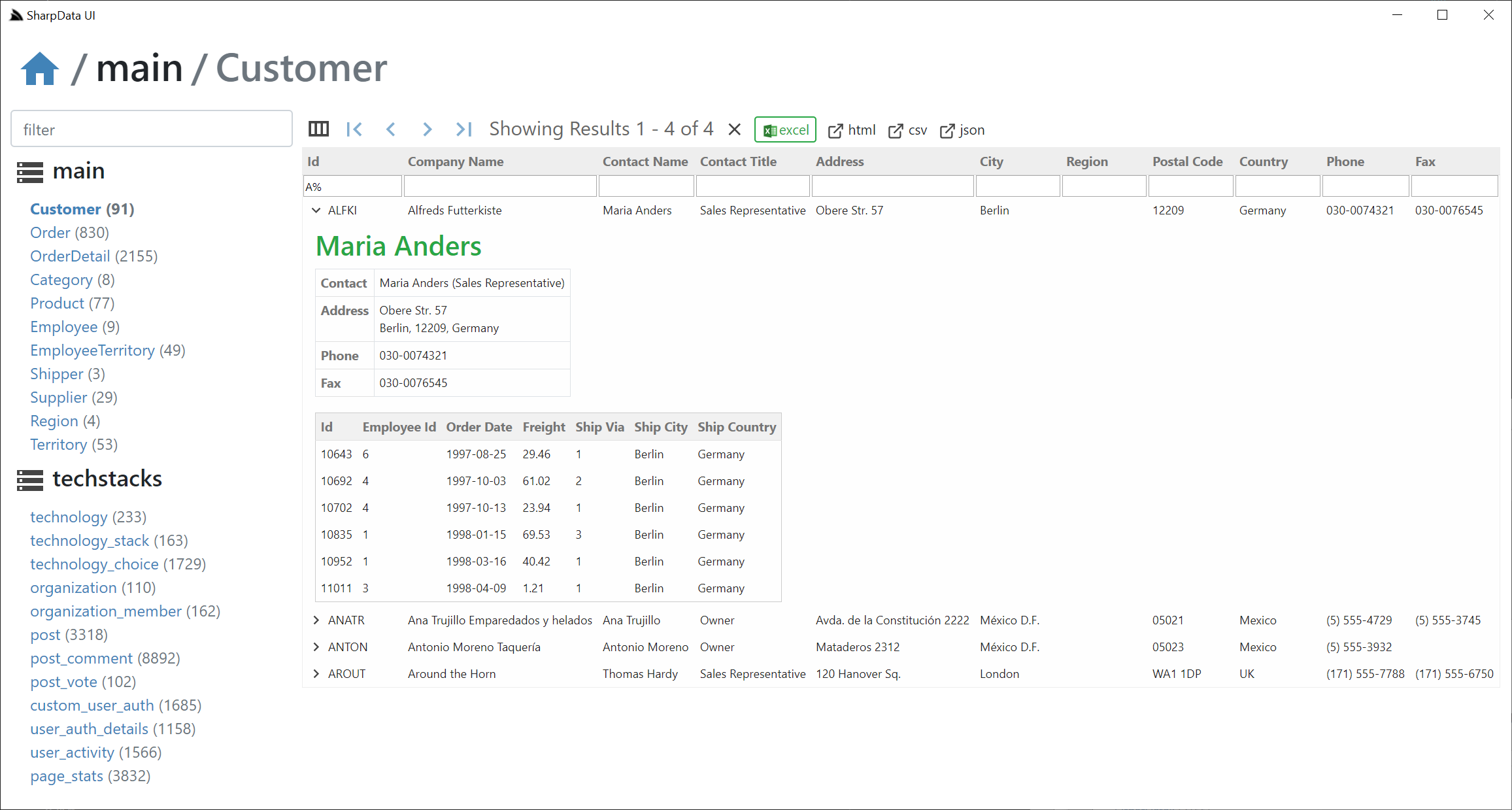
Where you can perform basic customizations like which RDBMS's and tables you want to be able to access, e.g:
debug false
name Northwind & TechStacks UI
appName sharpdata
db.connections[northwind] { db:sqlite, connection:'northwind.sqlite' }
db.connections[techstacks] { db:postgres, connection:$TECHSTACKS_DB }
args.tables Customer,Order,OrderDetail,Category,Product,Employee,EmployeeTerritory,Shipper,Supplier,Region,Territory
args.tables_techstacks technology,technology_stack,technology_choice,organization,organization_member,post,post_comment,post_vote,custom_user_auth,user_auth_details,user_activity,page_stats
Which will display both RDBMS Databases, showing only the user-specified tables in app.settings above:
Advanced Customizations
More advanced customizations can be added via dropping TypeScript/JavaScript source files in the /custom folder, e.g:
Which is how the northwind.sharpdata and chinook.sharpdata mix gists enable Customized Views for the Northwind & Chinook databases via their dbConfig registrations below:
chinook
dbConfig('chinook', {
showTables: 'albums,artists,playlists,tracks,genres,media_types,customers,employees,invoices'.split(','),
tableName: splitPascalCase,
links: {
albums: {
ArtistId: (id:number) => `artists?filter=ArtistId:${id}`
},
employees: {
ReportsTo: (id:number) => `employees?filter=EmployeeId:${id}`
},
invoices: {
CustomerId: (id:number) => `customers?filter=CustomerId:${id}`
},
tracks: {
AlbumId: (id:number) => `albums?filter=AlbumId:${id}`,
MediaTypeId: (id:number) => `media_types?filter=MediaTypeId:${id}`,
GenreId: (id:number) => `genres?filter=GenreId:${id}`,
}
},
rowComponents: {
albums: Album,
artists: Artist,
playlists: Playlist,
}
});northwind
dbConfig('northwind', {
showTables: 'Customer,Order,OrderDetail,Category,Product,Employee,Shipper,Supplier,Region'.split(','),
tableName: splitPascalCase,
links: {
Order: {
CustomerId: (id:string) => `Customer?filter=Id:${id}`,
EmployeeId: (id:string) => `Employee?filter=Id:${id}`,
ShipVia: (id:number) => `Shipper?filter=Id:${id}`,
},
OrderDetail: {
OrderId: (id:string) => `Order?filter=Id:${id}`,
ProductId: (id:string) => `Product?filter=Id:${id}`,
},
Product: {
SupplierId: (id:number) => `Supplier?filter=Id:${id}`,
CategoryId: (id:number) => `Category?filter=Id:${id}`,
},
Territory: {
RegionId: (id:number) => `Region?filter=Id:${id}`,
},
},
rowComponents: {
Order,
Customer,
}
});These db customizations let you specify which RDBMS tables & the order that they should be displayed, the table names text casing function, which columns to linkify & any custom Row Components for different tables.
Deploying Customizations
When deploying as a .NET Core project the customizations are deployed with your /wwwroot as normal.
To make customizations available to load with the SharpData Gist Desktop App you'll need to publish the directory of customizations to a gist. Here are the customizations for the northwind.sharpdata and chinook.sharpdata gists:
/dist-mix
-
/chinook
-
/custom
- chinook.js - UI Customizations
- app.settings - Custom App Settings
- chinook.sqlite - Embedded SQLite database
-
/custom
-
/northwind
-
/custom
- northwind.js - UI Customizations
- app.settings - Custom App Settings
- northwind.sqlite - Embedded SQLite database
-
/custom
You can publish a directory of files to a GitHub Gist using the x publish command with the
GitHub AccessToken with gist write access you want to write to, e.g:
$ cd northwind
$ x publish -token %TOKEN%
Viewing Customizations
When published these Gist Customizations can be viewed by gist id directly or by a user friendly gist mix or local alias:
- app://sharpdata?mix=0ce0d5b828303f1cb4637450b563adbd
- app://sharpdata?mix=96b10369daf94897531810841cb097f2
Custom Row Components
Whilst a tabular grid view might be a natural UI for browsing a database for devs, we can do better since we have the full UI source code of the Vue components. A filtered tabular view makes it fast to find the record you're interested in, but it's not ideal for quickly finding related information about an Entity.
To provide a more customized UX for different App UIs, SharpData includes support for "Row Components" (defined in /wwwroot/custom) to be able to quickly drill down & view richer info on any record.
For example when viewing an Order, it's natural to want to view the Order Details with it, enabled with the custom Vue component registration below:
@Component({ template:
`<div v-if="id">
<jsonviewer :value="details" />
</div>
<div v-else class="alert alert-danger">Order Id needs to be selected</div>`
})
class Order extends RowComponent {
details:any[] = [];
get id() { return this.row.Id; }
async mounted() {
this.details = await sharpData(this.db,'OrderDetail',{ OrderId: this.id });
}
}All Row components are injected with the db, table properties, the entire row object that was selected as well as the Column Schema definition for that table. Inside the component you're free to display anything, in this case we're using the sharpData helper for calling the server #Script HTTP API to get it to fetch all OrderDetail entries for this order.
If the resultset is filtered without the Order
IdPK it can't fetch its referenced data, so displays an error instead
The jsonviewer component used is similar to ServiceStack's HTML5 auto pages to quickly view contents of any object.
The registerRowComponent(db,table,VueComponent,componentName) API is used to register this component with SharpData to make it available to render any order.
With the Order component registered we can now drill down into any Order to view its Order Details:
You're free to render any kind of UI in the row component, e.g. here's the Customer.ts row component used to render a richer view for Customers:
@Component({ template:
`<div v-if="id" class="pl-2">
<h3 class="text-success">{{customer.ContactName}}</h3>
<table class="table table-bordered" style="width:auto">
<tr>
<th>Contact</th>
<td>{{ customer.ContactName }} ({{ customer.ContactTitle }})</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Address</th>
<td>
<div>{{ customer.Address }}</div>
<div>{{ customer.City }}, {{ customer.PostalCode }}, {{ customer.Country }}</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Phone</th>
<td>{{ customer.Phone }}</td>
</tr>
<tr v-if="customer.Fax">
<th>Fax</th>
<td>{{ customer.Fax }}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<jsonviewer :value="orders" />
</div>
<div v-else class="alert alert-danger">Customer Id needs to be selected</div>`
})
class Customer extends RowComponent {
customer:any = null;
orders:any[] = [];
get id() { return this.row.Id; }
async mounted() {
this.customer = (await sharpData(this.db,this.table,{ Id: this.id }))[0];
const fields = 'Id,EmployeeId,OrderDate,Freight,ShipVia,ShipCity,ShipCountry';
this.orders = await sharpData(this.db,'Order',{ CustomerId: this.id, fields })
}
}Which looks like:
SharpData .NET Core Project
Whilst NetCoreApps/SharpData can live a charmed life as a Desktop App, it's also just a regular ServiceStack .NET Core App with a Startup.cs and AppHost that can be developed, published and deployed as you're used to, here's an instance of it deployed as a .NET Core App on Linux:
sharpdata.netcore.io
For best experience we recommend running against local network databases
It's a unique ServiceStack App in that it doesn't contain any ServiceStack Services as it's only using pre-existing functionality already built into ServiceStack,
#Script for its HTTP APIs and a Vue SPA for its UI, so requires no .dll's need to be deployed with it.
It uses the same Vue SPA solution as vue-lite to avoid npm's size & complexity where you only need to run TypeScript's tsc -w to enable its live-reload dev UX which provides its instant feedback during development.
Some other of its unique traits is that instead of manually including all the Vue framework .js libraries, it instead references the new ServiceStack.Desktop.dll for its Vue framework libraries and its Material design SVG icons which are referenced as normal file references:
{{ [
`/lib/js/vue/vue.min.js`,
`/lib/js/vue-router/vue-router.min.js`,
`/lib/js/vue-class-component/vue-class-component.min.js`,
`/lib/js/vue-property-decorator/vue-property-decorator.min.js`,
`/lib/js/@servicestack/desktop/servicestack-desktop.min.js`,
`/lib/js/@servicestack/client/servicestack-client.min.js`,
`/lib/js/@servicestack/vue/servicestack-vue.min.js`,
] |> map => `<script src="${it}"></script>` |> joinln |> raw }}But instead of needing to exist on disk & deployed with your project it's referencing the embedded resources in ServiceStack.Desktop.dll and only the bundled assets need to be deployed with your project which is using the built-in NUglify support in the dotnet tools to produce its highly optimized/minified bundle without needing to rely on any npm tooling when publishing the .NET Core App:
<Target Name="Bundle" BeforeTargets="AfterPublish">
<Exec Command="x run _bundle.ss -to /bin/Release/net5/publish/wwwroot" />
</Target>The included /typings are just the TypeScript definitions for each library which TypeScript uses for its static analysis & its great dev UX in IDEs & VSCode, but are only needed during development and not deployed with the project.
Publish to Gist Desktop App
The primary way SharpData is distributed is as a Gist Desktop App, where it's able to provide instant utility by running on a users local machine inside a native Chromium Desktop App making it suitable for a much broader use-case as a fast, lightweight, always up-to-date Desktop App with deeper Windows integration all packaged in a tiny 20kb .zip footprint. There's no need to provision servers, setup CI, manage cloud hosting resources, you can simply run a script to update a Gist where its latest features are immediately available to your end users the next time it's run.
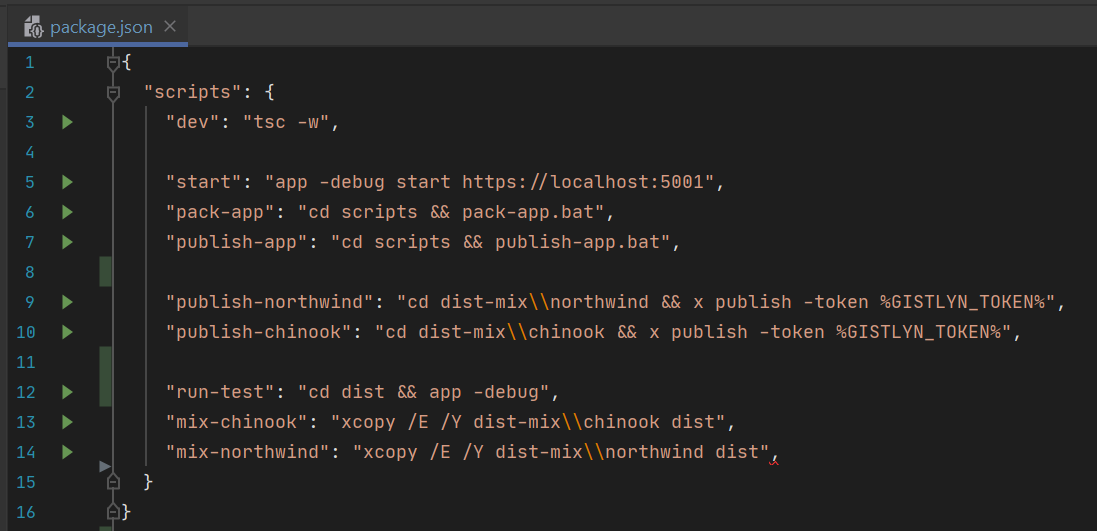
To run, test & publish it as a Desktop App you can use the pre-made scripts in package.json. Rider provides a nice UX here as it lets you run each individual script directly from their json editor:
Essentially to package it into a Sharp App you just need to run the pack script which will bundle & copy all required assets into the /dist folder which you can then test locally in a .NET Core Desktop App by running app in that folder:
$ cd dist
$ app
The mix-* scripts copies the db customizations so you have something to test it with which you can run with the run-test script.
The publish-app script is if you want to publish it to a Gist Desktop App, where you will need it to provide the GitHub AccessToken with write access to the Gist User Account you want to publish it to. Adding an appName and description to app.settings will publish it to the Global App Registry, make it publicly discoverable and allow anyone to open your App using your user-friendly appName alias, otherwise they can run it using the Gist Id or Gist URL.
Alternatively the contents of the dist/ folder can be published to a GitHub repo (public or private) and run with:
$ app open <user>/<repo>
Or link to it with its custom URL Scheme:
app://<user>/repo
If it's in a private repo they'll need to either provide an AccessToken in the GITHUB_TOKEN Environment variable or using the -token argument:
$ app open <user>/<repo> -token <token>
URL Scheme:
app://<user>/repo?token=<token>
RDBMS Configuration
When running as a .NET Core App you'd need to register which RDBMS's you want to use with OrmLite's configuration, e.g. the screenshot above registers an SQLite northwind.sqlite database and the https://techstacks.io PostgreSQL Database:
container.Register<IDbConnectionFactory>(c => new OrmLiteConnectionFactory(
MapProjectPath("~/northwind.sqlite"), SqliteDialect.Provider));
var dbFactory = container.Resolve<IDbConnectionFactory>();
dbFactory.RegisterConnection("techstacks",
Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("TECHSTACKS_DB"),
PostgreSqlDialect.Provider);By default it shows all Tables in each RDBMS, but you can limit it to only show a user-defined list of tables with #Script Arguments:
Plugins.Add(new SharpPagesFeature {
//...
Args = {
//Only display user-defined list of tables:
["tables"] = "Customer,Order,OrderDetail,Category,Product,Employee,EmployeeTerritory,Shipper,Supplier,Region,Territory",
["tables_techstacks"] = "technology,technology_stack,technology_choice,organization,organization_member,post,post_comment,post_vote,custom_user_auth,user_auth_details,user_activity,page_stats",
}
});When running as a Sharp App it's instead configured in its app.settings, here's equivalent settings for the above configuration:
# Configure below. Supported dialects: sqlite, mysql, postgres, sqlserver
db.connections[northwind] { db:sqlite, connection:'northwind.sqlite' }
db.connections[techstacks] { db:postgres, connection:$TECHSTACKS_DB }
args.tables Customer,Order,OrderDetail,Category,Product,Employee,EmployeeTerritory,Shipper,Supplier,Region,Territory
args.tables_techstacks technology,technology_stack,technology_choice,organization,organization_member,post,post_comment,post_vote,custom_user_auth,user_auth_details,user_activity,page_stats
Feedback
We hope SharpData serves useful in some capacity, whether it's being able to quickly develop and Ship a UI to stakeholders or as a template to develop .NET Core Apps that you can distribute as Sharp Apps, as an example to explore the delivery and platform potential of URL schemes and install-less Desktop Apps or just as an inspiration for areas where #Script shines & the different kind of Apps you can create with it.
Whilst app is Windows 64 only, you can use the x cross-platform tool and its xapp:// URL scheme to run Sharp Apps on macOS/Linux, it just wont have access to any of its Window Integration features.